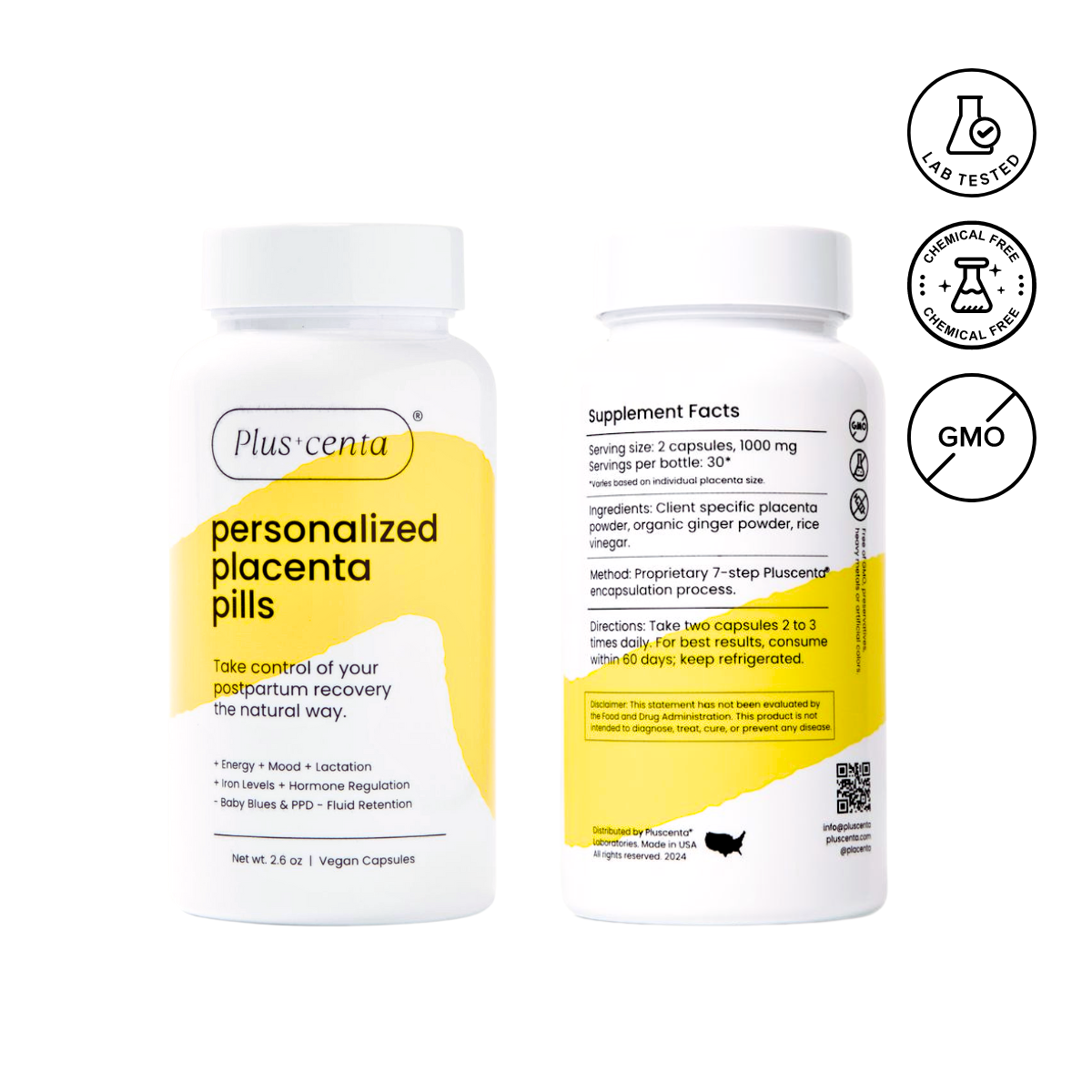
Why Choose Pluscenta for Placenta Encapsulation? Top Benefits Reported by Moms
Combat Fatigue
Oxytocin and corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) are proven to help combat fatigue and unlock new source of energy postpartum.
Increase Milk Supply
Your placenta contains high concentrations of prolactin. Prolactin helps promote lactation and increase overall milk supply.
Combat Baby Blues
Placenta consumption replenishes estrogen and progestrone which help stabilize postpartum mood,
Faster Wound Healing
Peer reviewed research has shown that several of the bioactive components of the placenta promote tissue regrowth and healing.